In 2021, cryptocurrency investments had high returns. Bitcoin rose by over 60 percent, Ethereum by more than 400 percent, and some smaller cryptocurrencies had returns in many thousands of percent.
Given these gains, you may be tempted to try to get in on the action.
At the same time, you may be concerned with your digital safety and security. How will you protect yourself against hackers and scammers? Will your privacy be protected? And how can you limit your exposure?
This article is a complete guide to keeping your crypto digitally secure. We’ll go over how to choose an exchange that is safe, how to store your crypto effectively, what kind of scams to look out for, and more.
In other words, we’ll touch on everything you need to know to shore up your digital security and invest in crypto safely.
An Overview of Crypto Safety in 2024
One key point to understand before diving into crypto is that it is not insured by the FDIC. You may lose everything if an exchange goes bankrupt or if a hacker manages to run off with your crypto. And when it comes to stolen or lost cryptocurrency, it is often impossible to get back.
I don’t say this to scare you, but it’s a reality that you should consider. Thankfully, there have been great developments in recent years concerning crypto safety.
The best way to protect your crypto investments is to take a multi-pronged approach.
- Only keep your cryptocurrency on an exchange if you’re trading it actively. Otherwise, transfer it to an external wallet.
- Take steps to make sure your exchange is secure, including using two-factor authentication.
- Take steps to secure your wallet by encrypting your keystroke file, keeping a paper backup of your seed words, and using a cold wallet if possible.
Don’t worry if it all sounds confusing right now. By the time you’re finished with this guide, you’ll be a crypto-safety pro.
What’s a Wallet: A crypto wallet is a device or piece of software that is used to make transactions on a cryptocurrency network. A wallet stores your “private key,” a string of characters used to prove that you are the owner of a particular cryptocurrency account.
Is Crypto Legal in the First Place?
Before we delve any deeper into crypto safety, let’s get into it with its legality. You want to make sure you’re not exposing yourself to scammers and hackers, but you also don’t want to run afoul of state and federal regulations.
As decentralized currencies, crypto is not and will likely never become banned in the U.S. Currently, the sale and purchase of cryptocurrency is legal in all 50 states. That being said, the government can – and does – regulate how virtual currencies are taxed and traded.
Existing Crypto Regulations
Cryptocurrency regulations in the U.S. are complex. There are several agencies involved in the regulation, and often, the differentiation in their power is not clear-cut. There are federal laws that oversee crypto trading companies, for instance, but each state can impose their own laws too.
In any case, here are the most important laws and regulations regarding cryptocurrencies you should know about:
- Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act: A small set of crypto provisions were added to the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act in 2021. According to the provisions, a person or company that “transfers digital assets on behalf of another person” is considered a broker and must now issue a Form 1099-B to each customer and to the IRS.
- Identity verification: In 2013, the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) started requiring cryptocurrency exchanges to keep documents proving the identity of their customers.
- SEC regulations: The Security and Exchange commission (SEC) has argued that some (but not all) cryptocurrencies can be considered as “securities,” thus, its developers must register with SEC.
In addition to those laws and regulations, investors must also check their own state laws regarding cryptocurrency. Doing so is also for your best interest; these regulations are in place as safety nets against the pitfalls of crypto trading, so if you stay on the good side of the law, you’re much better poised to trade crypto safely.
Are Offshore Exchanges Legal?
The short answer is “yes;” offshore exchanges are legal. They are simply exchanges operating outside of U.S. territory, which means they don’t have to comply with U.S. regulations. As such, investors enjoy greater convenience, a wider selection of coins, and better privacy as most offshore exchange companies don’t require identity verification.
That said, there are also great risks in using an offshore exchange. If an offshore exchange knowingly sells crypto to a U.S. resident, for instance, it may be fined by the FinCEN, and so offshore exchange companies may take steps to block users based in the U.S. That can make withdrawals difficult, or even impossible. So our advice? As much as possible, use an exchange recognized by the U.S. government.
FYI: There’s no explicit law prohibiting the use of offshore exchanges. However, legitimate exchange services outside the U.S. usually have measures to prevent U.S. residents from using their services to avoid incurring fines. It is also illegal to hide your assets held in an offshore exchange for the purpose of avoiding tax.
Crypto Safety: The Basics of Protecting Your Crypto
Protecting your digital assets, especially crypto, requires a conscious effort. You have to be proactive, because as we’ll discuss later on, once your crypto is stolen, it’ll be difficult to recover.
So here are some basic tips for protecting your crypto. Don’t fret if any of these tips are unclear, as we’ll dig in deeper later on.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA) on your wallets and exchange
- Withdraw your crypto from your exchange to a wallet.
- Write down the seed words for your wallet on a piece of paper, but store it safely.
- Use strong passwords every time. (Check your password strength here.)
- Use a unique password for your wallet; something not even remotely similar to other passwords you use.
- Store your crypto in a hardware wallet if possible.
- Avoid phishing and fake software or websites. Always be wary of crypto-related email files.
- Don’t enter your seed words on any website.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi, or if unavoidable, use a virtual private network service.
What to Look for in a Cryptocurrency Exchange and What to Steer Clear of
As you can see, there are many different things you can do to protect your digital assets, but perhaps one of the most important is choosing a legitimate and trustworthy cryptocurrency exchange. After all, it’s where you’ll buy and hold the crypto you’re trading.
Examples of Legitimate and Secure Crypto Exchanges
Luckily, there are plenty of legitimate, law abiding crypto exchanges. Some names that come to mind are Coinbase and Crypto.com. We’ll give you another one we’ve tried first-hand: Kraken.
Established in 2013, Kraken offers strong security and protection for your crypto investments.
- Cold wallets: 95-percent of Kraken’s crypto funds are stored in cold wallets, safe and out of reach of hackers.
- Server security: Kraken servers are in cages, physically monitored by security cameras and guards 24/7. Their physical locations are undisclosed, but Kraken promises that physical access to the servers are “strictly controlled.”
- 2FA: 2FA, short for two-factor authentication, protects users accounts from unsanctioned access.
- Bounty program and penetration tests: Kraken runs a bug bounty program and employs security experts to search for ways to penetrate the platform’s security in the hopes that vulnerabilities can be found and patched before the bad guys find them.
FYI: We have compiled a list of the best VPNs for crypto to help you have a more secure experience.
Security and reimbursement
When choosing an exchange to use, you should also consider how secure it is. In 2021, cryptocurrency exchange Bitmart was hacked and lost over $200 million worth of crypto.1
As we were preparing this article for publication, Crypto.com was also hacked for a loss of $35 million.
Both Bitmart and Crypto.com have promised to reimburse users who lost their funds.
In the past, other major exchanges have been hacked, including Binance, Bitfinex, KuCoin, and more. But these exchanges have all reimbursed users who lost funds.
One way of defending against security flaws is to find out how much of the exchange’s crypto is kept in “hot wallets” connected to the internet.
The best exchanges will keep only a small amount of crypto on these wallets. The rest will be stored off-line. This will limit losses in case a major hack occurs.
Another line of defense is to only use exchanges that reimburse users for hacks.
The better exchanges will have some kind of reserve fund they use to do this. If an exchange has been hacked in the past and has not reimbursed its users, this is a sure sign to steer clear of it.
Protecting Your Exchange Account With 2FA
Choosing a reputable exchange will help to protect you from attacks that are the exchange’s fault. But if your account is compromised through no fault of the exchange, you won’t be reimbursed.
This is why it’s important to enable 2FA.
If 2FA is enabled, you’ll be required to enter a code from a text message or mobile app every time you log in or make a withdrawal. This helps protect you from having your crypto stolen if your email account is compromised.
If 2FA is not enabled, an attacker who has access to your email account can use the “forgot my password” feature to change your password and lock you out of your account. The attacker can then safely transfer your crypto away while you watch helplessly.
If this happens, the exchange will usually not reimburse you for the loss.
Pro Tip: Text messaging should also not be used for 2FA if at all possible. This is because many attackers know how to use SIM hijacking to intercept 2FA codes from text messages. So using a mobile app like Google Authenticator for 2FA codes is a better option.
Storing Crypto Safely Using Wallets
While the above steps can help to protect you against an exchange attack, you are ultimately not in control as long as the exchange has your crypto. That’s where crypto wallets come in.
What Is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is like a literal wallet where you can store your cryptocurrencies, only, since cryptocurrencies are digital, crypto wallets are virtual as well. They are a piece of software you can use to prove that you are the owner of a particular crypto account or address. You can use a wallet to store cryptocurrency securely or to authorize crypto payments to employees or merchants.
Unlike exchanges, wallets live on your device, so the only way for an attacker to get crypto out of your personal wallet is to attack your personal device. While it is always possible that your device can be hacked, it is generally going to be less enticing of a target than your exchange is. So the most effective strategy you can use to protect your crypto is to move it into a private wallet.
>> Also check out: Is Crypto.com Safe?
Cryptography and How It Figures Into Crypto Wallets
Cryptography plays a huge role in cryptocurrency. Wallets use cryptography to authenticate transactions. When you create a wallet, it generates a hash of your “address,” which uniquely identifies your wallet. To send someone crypto, for instance, you’ll ask for their hashed address, and if someone is to send you crypto, you’ll give them your address.
The hash transmitted during transactions contain vital information – for example, the amount being transferred and the receiver’s address, signed using the sender’s private key – in code (encrypted). To interpret the code, validators will have to use a public key generated by the sender’s wallet, and for the transaction to push through, all the pieces of information must match.
That’s an over-simplification of the process. There’s a lot more that goes on in the background, but the bottom line is clear: Cryptography in wallets and the blockchain plays a major role in crypto security.
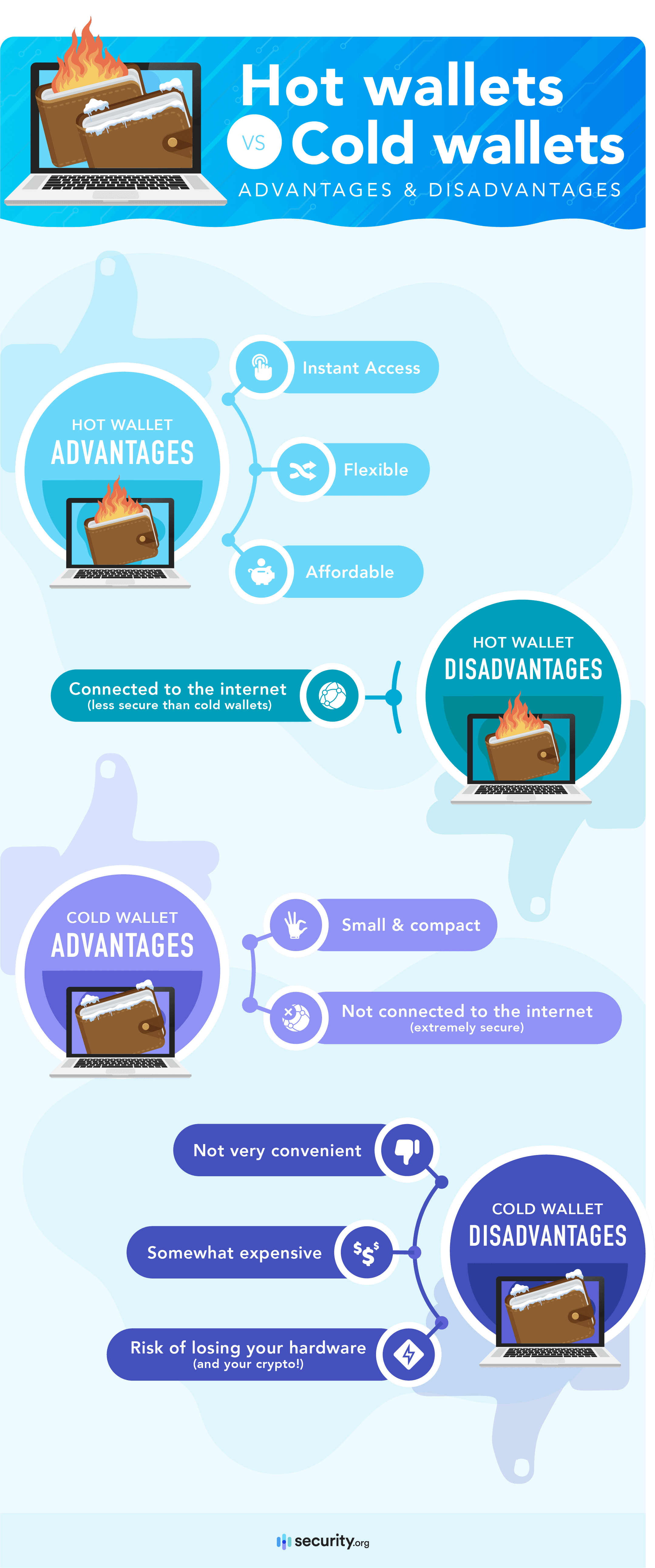
Hot wallets vs. cold wallets
Now, about the different types of crypto wallets, there are two you should absolutely know about before getting started: Hot wallets and cold wallets.
A hot wallet is a piece of software that runs on a device connected to the internet, such as a desktop or mobile wallet. You can download hot wallets from websites or from mobile app stores.
A “cold wallet,” on the other hand, is a wallet that is not connected to the internet. This includes paper wallets and hardware wallets. Cold wallets can’t be downloaded; they can only be purchased or created.
If you are going to be using your crypto on a daily basis, you may want to keep it in a hot wallet. But if you are just buying and holding, a cold wallet is the safer option.
Using a hot wallet to store crypto
To store your crypto in a hot wallet, first download it from the official website and run the setup file.
Setting up the app (seed words, passwords, and addresses)
When the app opens, it will display a set of seed words. These seed words are used to generate your crypto accounts and addresses.
Write down these words on a physical piece of paper in the order they are given to you. Do not take a screenshot of these words or store them on any kind of cloud service such as Dropbox or Google Drive.
Store your physical backup in a safe place where it cannot get wet, catch fire, or otherwise be destroyed. Don’t tell anyone where it is unless you intend for them to have access to your crypto.
Passwords
After allowing you to record your seed words, the app will ask you for a password. Use a strong password with numbers, capital and lowercase letters, and special characters if possible.
If you forget your password, you can restore your account using your seed words. So don’t stress about forgetting it. But make sure you don’t lose your physical copy of your seed words.
Addresses
When you finish this process, you’ll see your cryptocurrency address. It’s a long string of characters that is derived from your seed words.
When you withdraw your crypto, your exchange will ask for this string of characters. Make sure you copy and paste the address instead of hand-typing it. If you leave out or change even one character, you will lose the crypto you are sending!
Once your crypto is safely transferred into your wallet, the exchange will no longer have control over it. At this point, even if an attacker gets access to your exchange account, they will not be able to steal your crypto.
Understanding hot wallet security
Now that your crypto is in your hot wallet, you need to make sure it is protected from attacks.
The seed words you copied down on the piece of paper are used to generate an unlimited number of private keys. A private key is a string of characters your device uses to sign transactions and to prove that you’re the owner of the account.
Each private key corresponds to an account or address. You can create as many addresses as you want from a single set of seed words.
Your seed words are stored on your device in a file called a key vault. This file is encrypted with your password. When you make transactions or browse crypto-enabled websites, your wallet will ask for your password in order to decrypt this file.
For an attacker to get your crypto, they need to steal both your key vault and your password. If they only have one of these items, they can’t get your crypto. They need both.
There is a hash of your password on your device. If your password is weak and the attacker gets this hash, they might be able to crack it by guessing millions of random strings of characters until they find one that produces this hash. This is why using a strong password is important.
List of secure hot wallets
Here is a chart showing some of the most secure hot wallets. In each case, we’ve provided a link to the official website where an authentic copy of the software can be downloaded. We’ve also listed the type of wallet (desktop or mobile) and the networks it can be used on.
Software Crypto Wallets
| Wallet | Type | Networks | Official website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrum | Desktop | Bitcoin | Electrum.org |
| Mycelium | Mobile | Bitcoin | Mycelium.com |
| Exodus | Desktop and mobile | Multiple | Exodus.com |
| Metamask | Desktop and mobile | Ethereum, BSC, Avalanche, HarmonyONE | Metamask.io |
| Brave Browser | Desktop and mobile | Ethereum, BSC, Avalanche, HarmonyONE | Brave.com |
| Coinbase wallet | Desktop and mobile | Ethereum, BSC, Avalanche, HarmonyONE | Coinbase.com/wallet |
Using a cold wallet to store crypto
Hot wallets can be extremely secure if you use them correctly, but they can still be compromised if your device becomes infected with keystroke logging software. This is where using a cold wallet can help to protect you further.
If used correctly, a cold wallet should be impossible to hack except through physical theft.
Hardware wallets
The most popular form of a cold wallet is a hardware wallet. A hardware wallet is a small USB device that stores a keystore file. If you want to make a transaction with a hardware wallet, you can attach it to your PC or mobile device and send a signature through the USB port.
However, the key vault is stored on a separate memory bank in the device and can’t be transmitted through USB in an unencrypted form. This means that even if an attacker infects your PC with malware, they should be unable to gain access to your crypto.
The biggest risk to using a hardware wallet is physical theft. To further protect against even this possibility, hardware wallets have pin code locks.
Security experts have been able to hack hardware wallets using very sophisticated techniques once they had physical possession of them. So if you lose your hardware wallet, it’s best to transfer your crypto out of the wallet as soon as you realize it’s missing.
The biggest disadvantages to hardware wallets are inconvenience and cost.
If you use a hardware wallet, you have to connect the wallet to your PC and confirm the transaction using both the USB device and the software running on your PC. This can be quite inconvenient if you make a lot of transactions.
In addition, hardware wallets usually cost from $49-$220. So they are not economical for storing very small amounts of crypto.
List of hardware wallets
Here is a list of some of the more popular hardware wallets. We’ve included main features and prices for these as well.
Hardware Crypto Wallets
| Model | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Trezor Model T | Supports all major networks; large, full-color touch screen (no buttons) | $185-$220 |
| Ledger Nano X | Supports all major networks; Bluetooth for mobile devices, large buttons, black & white OLCD screen | $119-$149 |
| Ledger Nano S | Supports 27 different networks; small buttons, black & white OLCD screen | $59 |
| Keepkey | Supports 7 different networks; small buttons, large OLCD screen | $49 |
Paper wallets
Another form of cold wallet is a paper wallet. A paper wallet is a private key and address that are only stored on a piece of paper. Since the key is not stored on any kind of computing device, it should be impossible for a hacker to steal it.
In the early days of Bitcoin, paper wallets were very popular as a method of storage.
But unfortunately, this method turned out to have one big security flaw: in order to generate the key and address, you needed to download an app into your browser. And it was difficult to know if the app was sending your keys to the web server and exposing your account.
Today, paper wallets should not be considered secure.
Now that we’ve got the basics of wallets out of the way, let’s discuss some common crypto scams to watch out for.
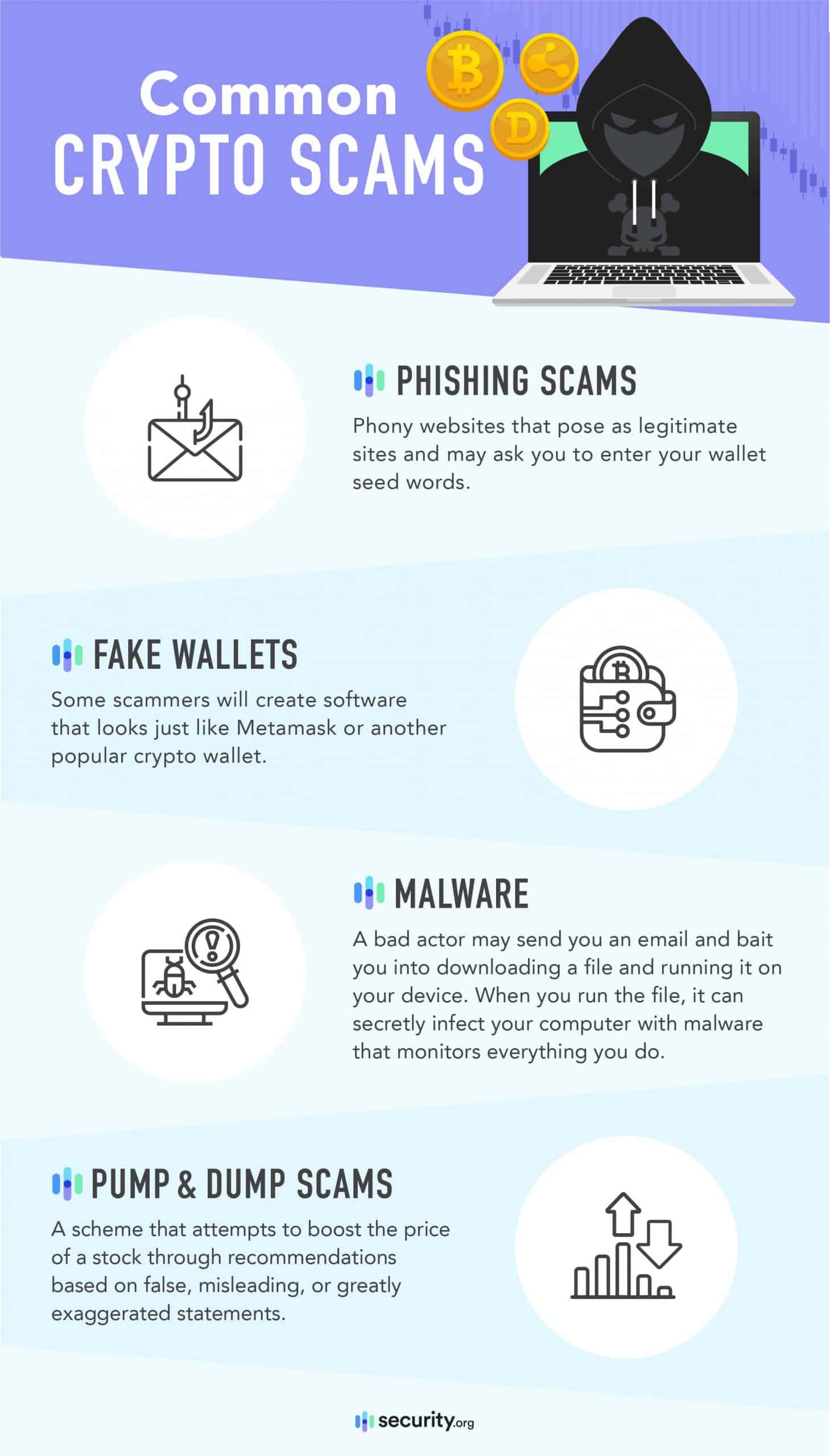
Common Crypto Scams
Even if you store your crypto in a private wallet, it’s still possible to fall for common crypto scams if you don’t know what they are. So here are a few things to be aware of.
Crypto website phishing scams
There are a lot of phony websites that will pose as legitimate sites and ask you to enter your wallet seed words. This kind of fraud is called a “phishing site,” and it’s a common type of crypto scam.
For example, you may think you’ve gone to the official Uniswap app at app.uniswap.org, but you’ve actually gone to app.uniswop.org instead (notice the spelling!). If a hacker sets up a website to look exactly like the official site, but on a slightly different URL, they may convince you that you’re interacting with the official site.
It’s especially easy to avoid crypto website phishing scams though. Just be sure to never enter your seed words or private key into any field on any website. Even if it looks like your wallet itself is asking for your seed words as you are browsing the web, don’t enter them.
If you forget your password or otherwise get locked out of your account, first delete your wallet from your device. Then, reinstall the wallet.
Once it’s reinstalled, you can safely enter your seed words into the wallet to recover your account. But this should be done from a blank page in your browser, not from an actual page on the web. And it should only be done once, right after installing.
Did You Know? Your wallet will ask you for your password often. But it will never ask you for your seed words as you are browsing the web. Seed words are only required during installation.
Fake wallets
Another common crypto scam is fake wallets.
Some scammers will create software that looks just like Metamask or another popular crypto wallet.
They’ll advertise their “wallet” in places like Google Ads or Facebook. When you click through the ad and visit the site, you’ll be given a link where you can download what you think is a legitimate copy of the software. But in reality, this software has been altered so that once you generate your seed words, it will send them to the scammer. Now all they have to do is wait until you send some crypto to the wallet; when you do, the attacker will transfer it to their own wallet.
The best way to protect against this kind of attack is to only download your wallet from the official website.
Google places its ads above the organic search results, so if you search for a wallet, make sure you scroll down to the organic results instead of clicking an ad. Wallets generally do not advertise. So if you see an ad for a wallet, it’s probably a scam.
Also, don’t search for a wallet from within the Google or Apple app stores. These stores have been known to place scam wallets at the top of their results in the past (probably not intentionally). Instead, go to the wallet’s official website. From there, click the link to get to the Google or Apple app store page for the wallet.
Malware
Another common crypto scam is to simply infect your computer with malware. A bad actor may send you an email and bait you into downloading a file and running it on your device. When you run the file, it can secretly infect your computer with malware that monitors everything you do.
We’ve already talked about malware in other sections, so we won’t spend much time on it here. But here are a few short tips to protect against losing your crypto to a malware attack.
- Don’t use a wallet password that is the same as a stored website password
- Don’t take a screenshot of your seed words
- Don’t download files from emails unless you’ve verified the address
- If possible, check your inbox on a different device from the one you use for crypto
- If possible, use a hardware wallet
Even if you take these steps to protect your seed words, you may wonder if there is some way for a hacker to steal your crypto anyway. Can a crypto network itself be hacked? Can an attacker transfer your crypto to themselves even if they don’t have your seed words or private key? For answers to these and other questions, read below.
Can Crypto Networks Be Hacked?
On centralized networks like PayPal or banks, an attacker may be able to gain access to your account even if you keep your password completely secure. This is because the network itself may have a security flaw that can be exploited.
You may wonder if crypto networks can suffer from similar flaws that will allow an attacker to transfer your funds without having your private key.
In other words, can crypto networks be hacked?
The short answer is “no.” Under most circumstances, there is simply no way for an attacker to steal another person’s crypto without having that person’s private key. So if you are just holding crypto in your wallet, there is no known way for a scammer to steal it without getting your key. Here’s why:
Shared database
On a crypto network, all of the nodes have a copy of the database. If an attacker alters the balances on one copy, the copies stored by other nodes will show a discrepancy. As a result, the hacked node’s copy of the database will be rejected by them.
Signatures
Each transaction is required to have a valid “signature,” a message encrypted with the owner of the account’s private key. If a node claims that a particular transaction is valid, all other nodes on the network will expect to see a signature proving that the transaction is valid.
If the signature can’t be produced, the rest of the network will reject the transaction.
This is why a hacker needs your private key in order to steal your crypto. Even if the hacker is running a validator service and is therefore “in charge” of the network, they still can’t transfer your crypto without your consent. Because the network is decentralized, even the people validating transactions don’t have the power to break the rules.
Want to know more about how crypto transactions are secured? Check out our crypto user’s guide to cryptography.
Double-spend attacks
Of course, a hacker might be able to spend their own cryptocurrency and then erase the transaction. This is called a “double-spend attack.”
In order to perform a double-spend attack, the malicious node needs to somehow make its transaction history longer than every other node. If it can pull this off, it can get its own fraudulent copy of the database accepted as the real one. So it will need to add a bunch of spam transactions to its database if it wants to accomplish this.
Cryptocurrency networks defend against double-spend attacks using various techniques. For example, the oldest crypto networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum require nodes to spend a bunch of electricity on a complicated math problem each time they add transactions to the ledger. This makes it so expensive to produce spam transactions that the attacker would probably lose more money on electricity than they would gain from the fraud.
Newer networks like Avalanche, Binance Smart Chain, and Ethereum 2 tackle the problem in a different way. They require each node to put up a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a bond, and each node has to sign every block of transactions it wants to add to the ledger. If a validator tries to double-spend, any other node can easily detect this and submit proof of it to the network.
If a node is caught trying to double-spend on these networks, it has its bond taken from it and given to the validator who discovered the fraud. Because of this incentive, double-spends are extremely difficult to pull off on these newer networks.
The bottom line is that double-spend attacks are not a problem for most users because most users are not selling goods in exchange for crypto.
And there is no other known vulnerability in crypto networks. So essentially, crypto networks cannot be hacked.
Crypto Pitfalls to Avoid
That said, there’s a way you could lose your cryptocurrency, and it doesn’t involve complex hacking techniques. We’re talking about investing mistakes. To cap off this guide, here are some crypto investing pitfalls to avoid. After this, you’ll be ready to embark on your crypto journey.
- Not considering volatility: Crypto prices rise and fall, sometimes sharply. Investors sometimes buy too much thinking they can sell for cash if they need to, and then they have to sell at a loss.
- Not realizing transactions are irreversible: Crypto transactions are usually not reversible because nobody has the authority to issue the reversal. So before making any transaction, check everything, and then check again.
- Failing to do your research: It’s easy to forget to do all this research when you see five YouTube videos in the same day by people who claim to be making phenomenal returns on the latest crypto-based craze, only to fall for a false hype. Always do your due diligence before investing.
- Overtrading: The crypto market is unpredictable. No one can predict where it will go in the next day or even the next hour. For most investors, the safest option is to buy assets that have good utility and hold them for years. That strategy is slow and boring, but it’s usually the most profitable.
- Falling for Ponzi or MLM schemes: There’s no such thing as a risk-free get-rich-quick scheme, not even in crypto. If a cryptocurrency promises to yield returns too good to be true, there’s likely a huge risk involved or it’s downright a Ponzi scheme.
- Falling for a rug pull: A rug pull is a scam in which the project founder invites users to invest crypto in the project, and then runs off with the crypto once enough investors have piled in. It’s pretty simple, but many still fall for it.
Wrapping Up
Crypto can seem like an especially risky investment to hold compared to other assets. Other assets only carry the risk of going down in price. With crypto, there seems to be the additional risk of hacking and digital theft.
But investing in crypto doesn’t have to be especially risky. By taking the proper steps to protect your digital currency, and making sure you don’t take on undue legal risks while investing, you can minimize the risk of losing it to hacking or scams.
FAQs
See below for answers to a few frequently asked questions about investing in crypto safely.
-
Are crypto exchanges safe for long-term storage?
No. Crypto exchanges are as safe as they can be, but they face some unique problems compared to stock exchanges.
Crypto exchanges allow you to withdraw crypto into your own possession. As long as this is possible, there is always the chance that an attacker can transfer your crypto into their own hands. The best way to protect yourself against this threat is to move your crypto into your own wallet.
-
Are crypto investments insured?
Under most circumstances, cryptocurrency investments are not insured. Some exchanges may insure your crypto in case your exchange is hacked. But if the theft wasn’t the exchange’s fault, the insurance usually won’t pay.
-
What is a crypto wallet?
A crypto wallet is a piece of software or device that stores your private key or seed words. If you want to perform cryptocurrency transactions, you need a wallet. If used correctly, wallets are also a very secure way to store cryptocurrency.
-
What is a cold wallet?
A cold wallet is a crypto wallet that is not connected to the internet. Some examples include a hardware wallet, a piece of paper with a private key on it, or a laptop that has a private key on it but no network adapter.
Cold wallets are especially secure ways to store crypto. Because they are not connected to the internet, they cannot be hacked remotely, although they can still be physically stolen.