Virtual Reality Awareness and Adoption Report
An estimated 53 million adults own VR systems, and an additional 14 million could purchase over the next six months.
Long regarded as sci-fi aspiration, virtual reality (VR) has evolved into a viable platform for entertainment, communication, and education. What once required expensive hardware and technical expertise has transformed into an accessible technology that fits in your living room. Industry giants like Meta, Apple, and Sony are betting billions that VR will reshape how we work, play, and connect.
Yet as Big Tech prominently promotes virtual reality as a portal to humanity’s future, people also have reservations about its safety and security. Our recent study reveals Americans’ experiences with this emerging technology and their concerns about its future.
Key Findings:
- An estimated 53 million US adults currently own a VR system, and 8 percent of non-owners said they are likely to purchase one in the next six months. This could translate to an additional 14 million new customers – representing 21 percent growth in the U.S. market.
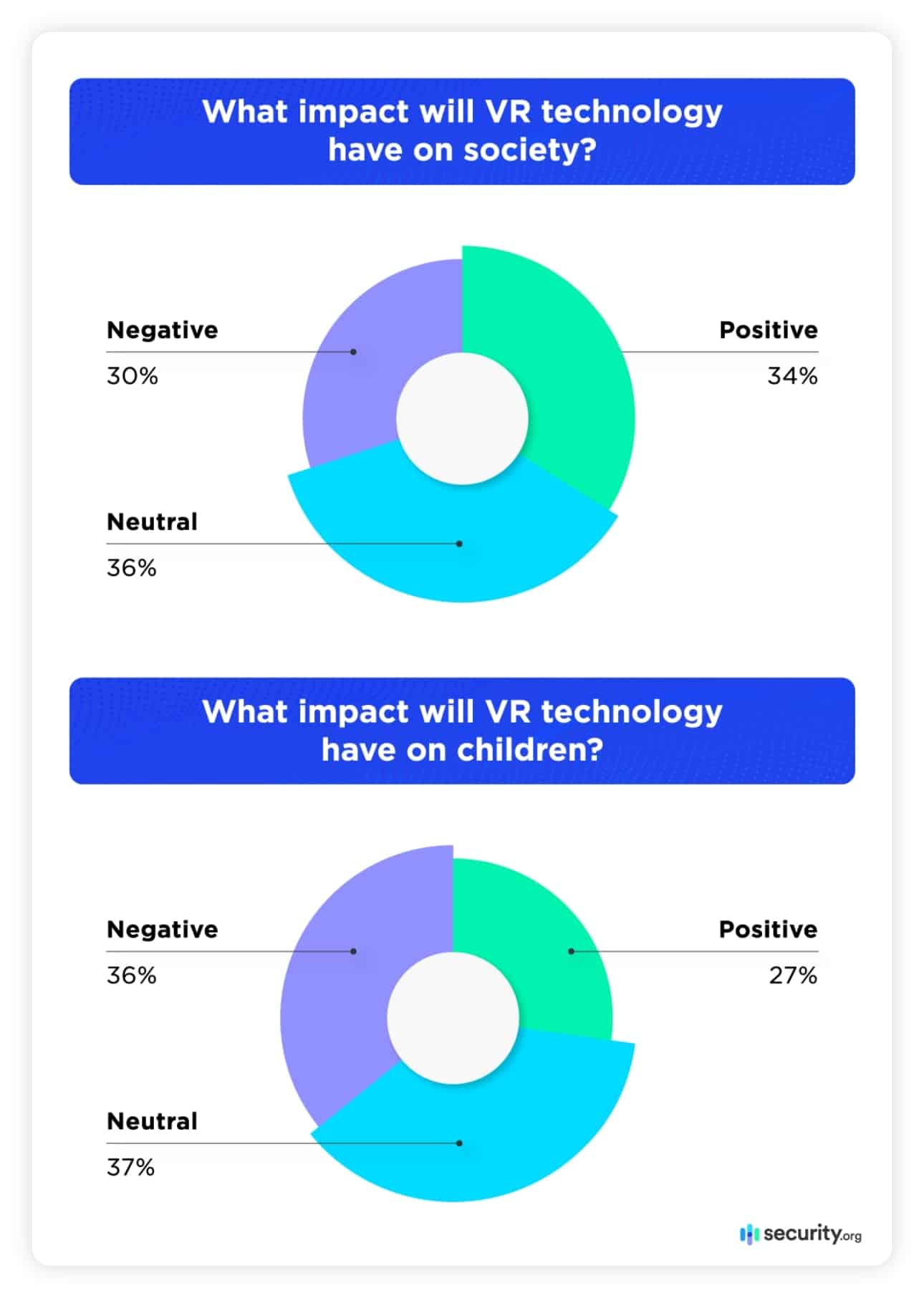
- Public concern about VR technology gives different insight compared to growing curiosity: only one in three Americans believe that VR will have a positive impact on society.
- Most Americans are not seriously concerned about the security and privacy of VR technology. That said, many are particularly concerned about the tracking of their biometric data.
Virtual Reality Market is Poised to Increase
Think of virtual reality as your personal holodeck. It’s a technology that creates convincing digital worlds you can step into and interact with. Unlike watching a screen, VR surrounds you completely, tracking your head movements and hand gestures to make you feel genuinely present in a virtual world.
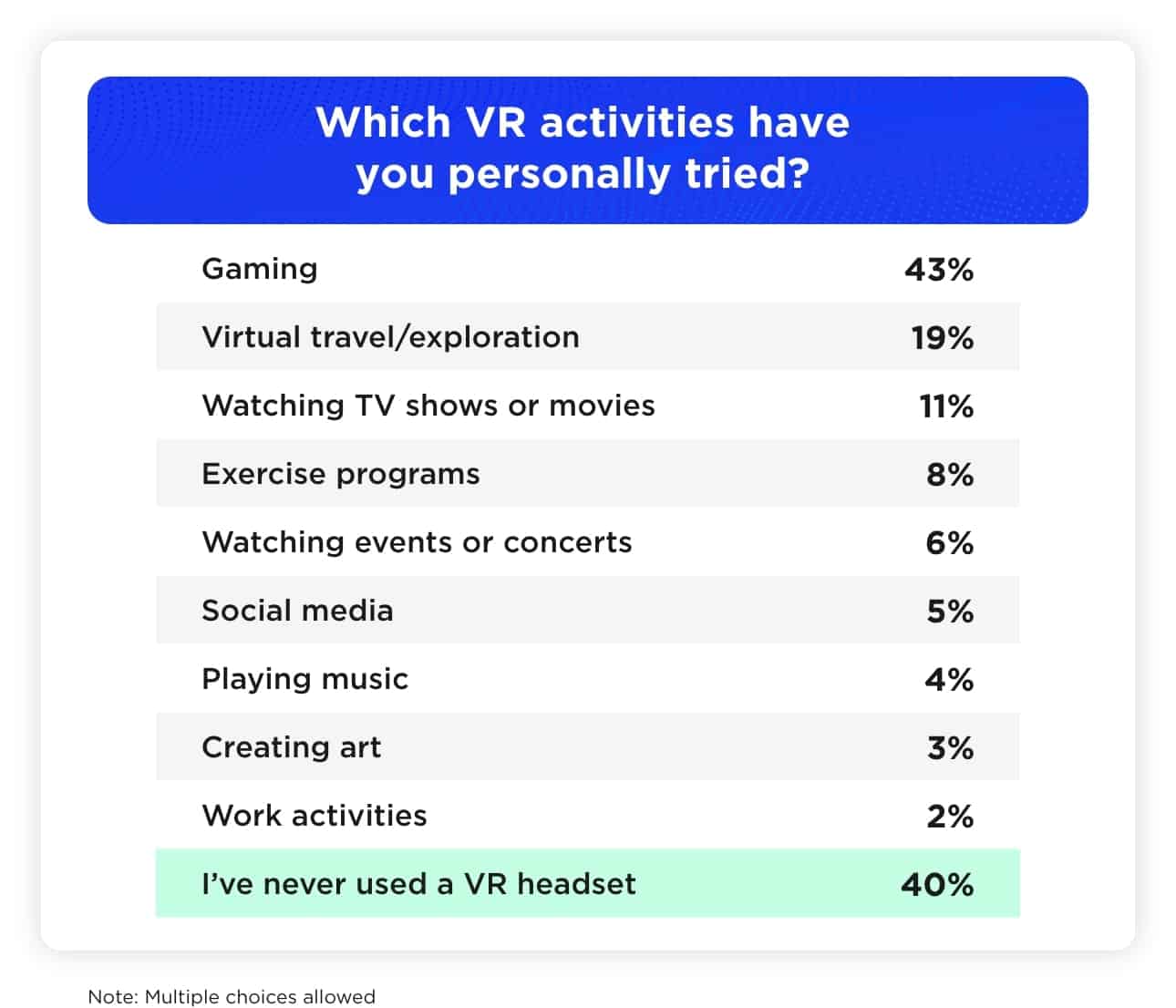
Thanks to expanded accessibility, more than half of U.S. adults (an estimated 140 million) have already experienced virtual reality, most likely through widely accessible headset-style devices. The most popular application has been VR gaming, but many have tried other activities, such as virtual “travel” or streaming TV and movies.
While a majority of adults have tried out the tech, 23percent of Americans currently own a VR device. This represents approximately 53 million US adults.
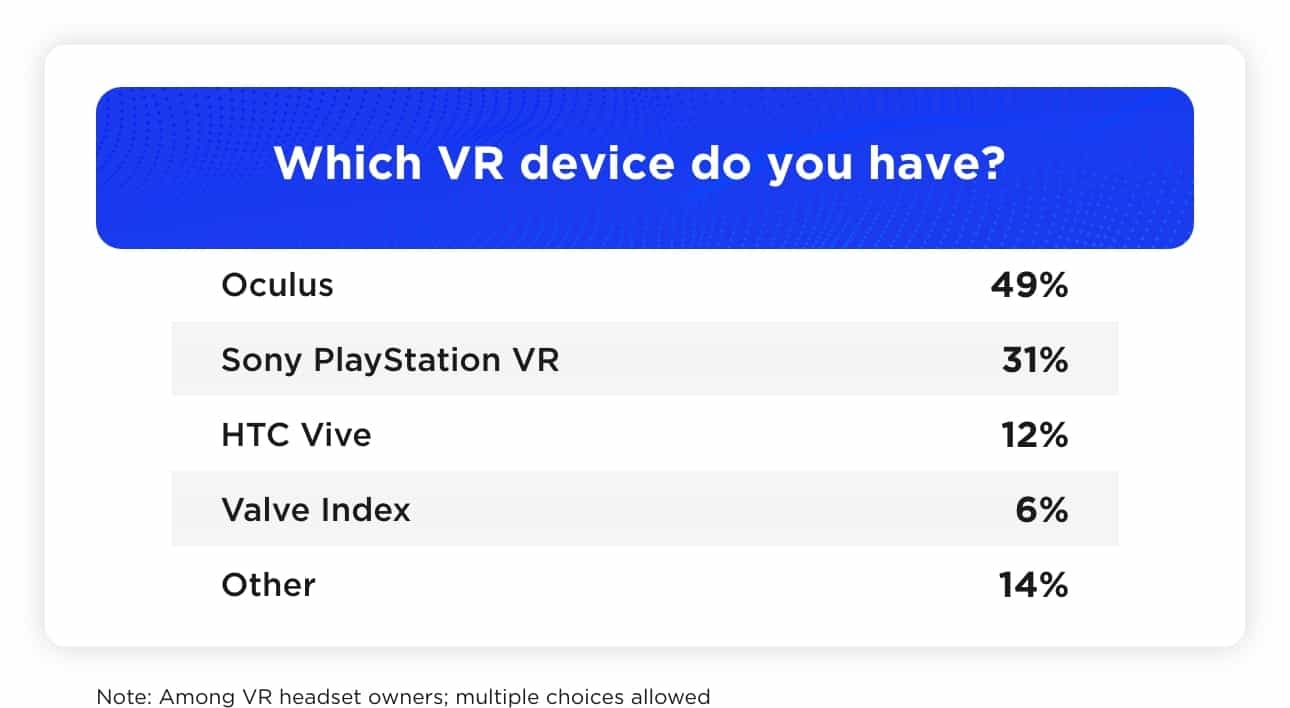
According to our research, Meta’s Oculus dominates nearly half of the market among current owners. In just three months of 2025, Meta sold 710,000 VR headsets, maintaining its lead despite an increasingly competitive landscape.1
VR headset owners are increasingly satisfied with their purchases. About 80 percent of owners report satisfaction with the graphic quality of their devices. That’s even higher with newer models featuring 4K displays and improved refresh rates. However, not as many users are pleased with the library of apps, which now includes productivity tools, fitness programs, and social experiences beyond gaming.
As interest in VR technology accelerates, adoption of personal VR devices shows strong momentum. Our research revealed that 8 percent of those without their own VR headsets are likely to buy one in the next six months. This could equate to 27 million new customers – a nearly 50 percent growth in the market. That’s partly driven by more affordable options and compelling new applications.
Despite the potential for rapid market growth, many consumers aren’t ready to jump on the VR bandwagon. Cost remains the most significant barrier for potential buyers. Personal VR devices range from under $20 for rudimentary devices up to thousands for Apple’s Vision Pro, with most quality headsets falling between $500 and $1,000. While cost is an issue for some, others simply have no desire to own a device. There are also people with concerns about the potential effects of VR technology.
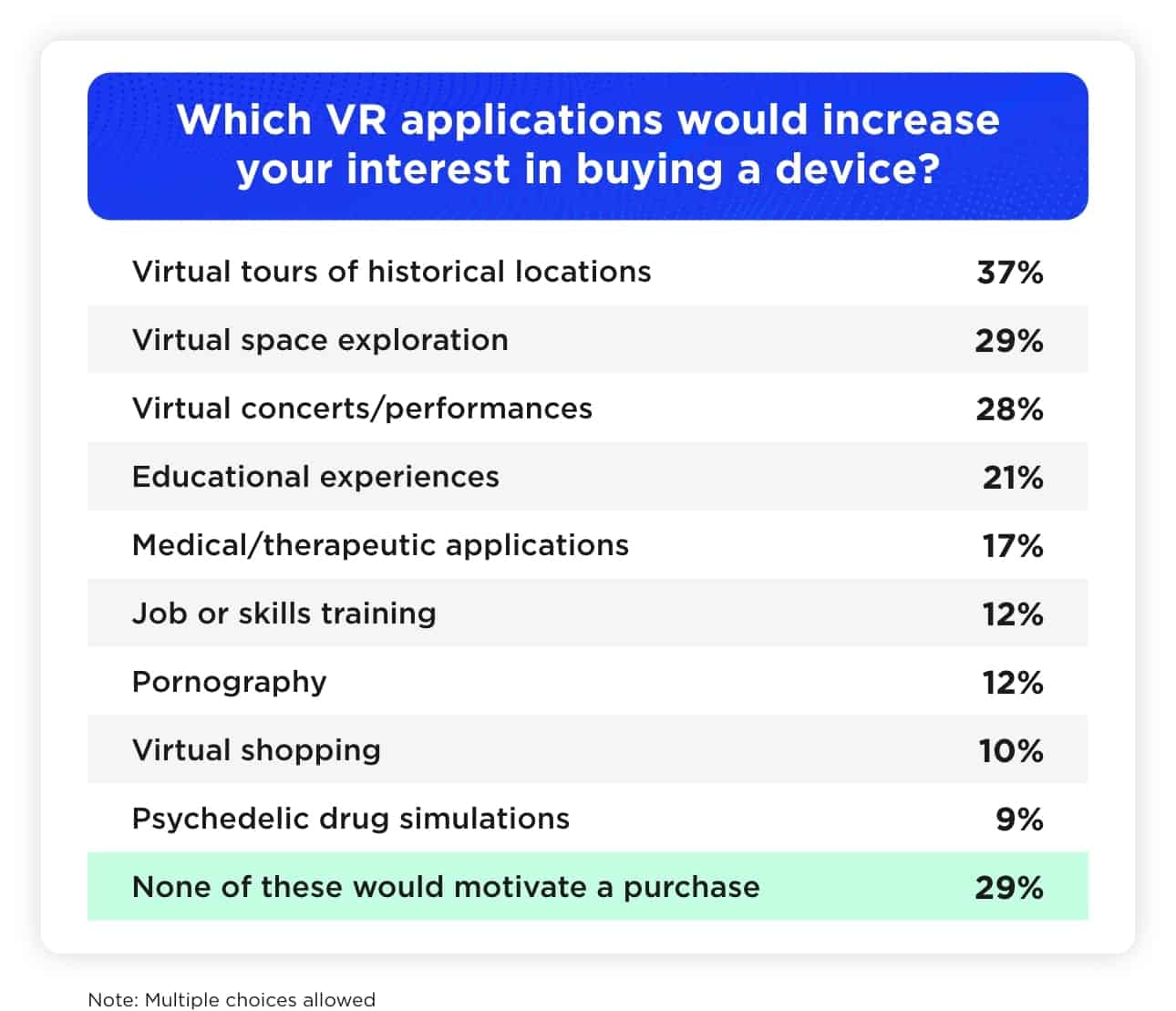
Some purchase barriers are disappearing as manufacturers address consumer concerns. Better comfort designs, wireless connectivity, and standalone operation (no computer required) have made VR more appealing. Among those without their own headsets, 71 percent indicated that emerging virtual reality experiences could motivate them to buy a device.
Virtual history tours and space exploration are among the most enticing possibilities.
Despite Widespread Interest, Consumers Have Hesitations About VR Security
The combination of improved hardware, sophisticated software, and widespread 5G connectivity transformed virtual reality from a niche technology to a mainstream platform. With applications expanding into healthcare, education, and remote work, VR is poised to become as common as smartphones in our daily routines.
While virtual reality’s potential appears limitless, the same may be said of its dangers. Beyond physical challenges like motion sickness and spatial disorientation, serious concerns exist about data privacy, psychological impacts, and the potential for addiction. This is particularly concerning for younger users who may struggle to distinguish virtual experiences from reality.
Even as respondents exhibited interest in VR possibilities, they expressed societal concerns. Americans are evenly divided about whether virtual reality’s impact will be positive or negative.
Americans were more concerned about the impact of VR technology on children. Overall, 36 percent believe VR use will negatively impact children’s development. Apprehension was strongest among the youngest generation in our study. Members of Generation Z (aged 18-25) showed far more concern about childhood repercussions than members of older generations.
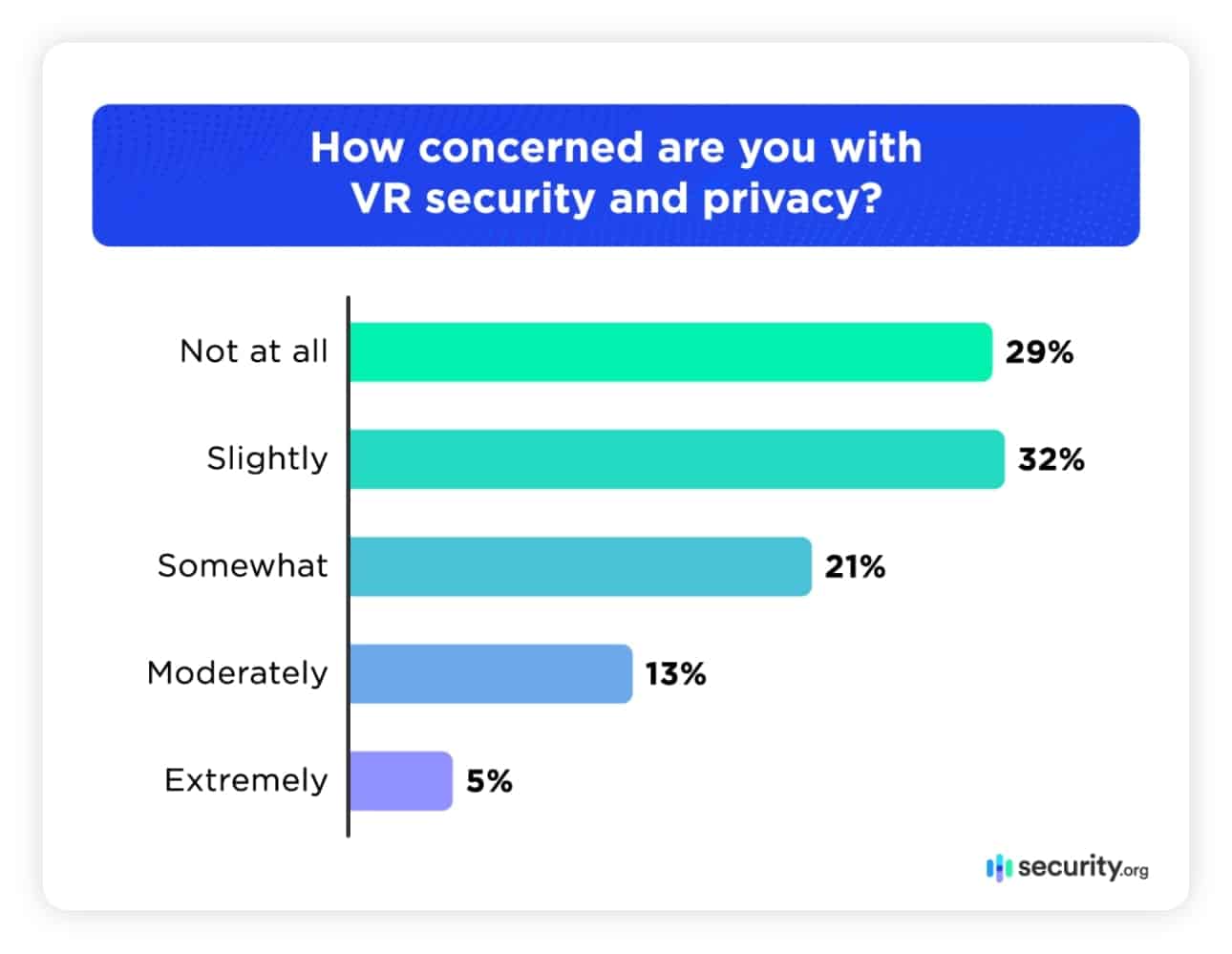
In an age rife with malware, data breaches, and other cyber attacks, consumers are also worried about VR integrity and exchanging data in virtual spaces. Nearly one in five people were moderately or extremely concerned about the security and safety of the technology.
The most common worry was data breaches, followed closely by the tracking of biometric data. Modern VR headsets track where you look, monitor eye movements, map room layouts, record voice patterns, and even measure pupil dilation. This biometric goldmine creates an incredibly detailed profile of users that, if compromised, could enable sophisticated identity theft or manipulation.
In addition to problems related to society and security, virtual reality can inflict more personal, physical damage. Some have been injured due to crashing into real-world objects while lost in an alternate universe, and 62 percent of VR users have experienced nausea or dizziness while wearing a headset.
Safety and Security Tips for VR
Protecting yourself in virtual reality requires the same vigilance you’d apply to any connected device, plus some VR-specific precautions, including:
- To guard against thievery and snooping in the metaverse, connect through a secure VPN. If your VR headset is connected to a computer, you can easily install a VPN and connect the computer to it to make your network private. For VR headsets that connect to the internet directly, you can set up a VPN router.
- When shopping through VR applications, use the same password security measures as you would for your phone or computer.
- Start with short sessions (15-20 minutes) and gradually increase duration to limit discomfort while wearing a headset. Ensure proper interpupillary distance (IPD) adjustment, maintain at least 90Hz refresh rate when possible, and take breaks every 30 minutes to prevent eye strain.
- Only use VR devices in a setting that is free of obstructions like furniture, walls, pets, or other people. Use guardian boundaries or play space markers, keep a small fan pointed at you to maintain orientation, and consider using a textured mat to define your safe zone.
- Stop using VR immediately if you experience persistent nausea, headaches, or disorientation.
Outlook
After years of false starts and unfulfilled promises, virtual reality has finally reached a tipping point. The technology that once required a $10,000 investment now costs less than a gaming console. It can also deliver experiences that have evolved from tech demos to genuinely useful applications.
Many Americans remain cautiously optimistic about VR’s role in their lives. Current devices are becoming more affordable and versatile. However, potential buyers still cite concerns about content variety, physical comfort, and long-term health effects. As competition intensifies, we’re seeing rapid improvements in all these areas – suggesting that today’s hesitant observers may become tomorrow’s enthusiastic adopters.
Looking ahead, VR’s integration into professional training, remote collaboration, and therapeutic applications signals a shift from entertainment gadget to essential tool. Major corporations are already conducting meetings in virtual spaces, surgeons are practicing complex procedures in VR, and therapists are treating PTSD with controlled virtual environments.2
How successfully VR transitions from curiosity to necessity will depend on addressing legitimate security concerns, establishing clear privacy standards, and ensuring the technology enhances rather than replaces human connection. The metaverse may not become our entire lives, but it’s increasingly becoming a meaningful part of them.
Our Data
Security.org conducted an internet-based survey of 1,010 U.S. residents in March 2022. Participants’ genders, ages, and ethnicities/races were representative of the population of the U.S and user estimates were also based on the number of Americans with internet access in the U.S. from broadbandnow.com.
Citations
- Counterpoint Research. (2025). Global XR (AR & VR Headsets) Market Share: Quarterly.
https://counterpointresearch.com/en/insights/global-xr-ar-vr-headsets-market-share-quarterly - Implementation Science Communications. (2023). Implementation of virtual reality in healthcare: a scoping review on the implementation process of virtual reality in various healthcare settings.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10276472/